Nuclear fusion
The nuclear fusion process occurs in elements that have a low atomic number such as hydrogen. Nuclear fusion is the process by which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a single heavier one while releasing massive amounts of energy.

Nuclear Fusion 7 3 4 Edexcel Igcse Physics Revision Notes 2019 Save My Exams
In cases where the interacting nuclei belong to elements with low atomic numbers eg hydrogen atomic number 1 or its isotopes deuterium and tritium substantial amounts of energy are released.

. Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles neutrons or protons. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in nuclear binding energy between. Researchers focus on DT reactions both because they produce large amounts of energy and they occur at lower.
The approach which gives rise to the heat and. 1 day agoIgnition confirmed in a nuclear fusion experiment for the first time A 2021 experiment achieved the landmark milestone of nuclear fusion ignition which data analysis has now confirmed but. 17 hours agoNuclear fusion involves smashing together light elements such as hydrogen to form heavier elements releasing a huge burst of energy in the process.
Nuclear fusion process by which nuclear reactions between light elements form heavier elements up to iron. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. Fusion reactions take place in a state of matter called plasma a hot charged gas made of positive ions and free.
In a potential future fusion power plant such as a tokamak or stellarator neutrons from DT reactions would generate power for our use. Nuclear fusion is a reaction through which two or more light nuclei collide to form a heavier nucleus. In the process it also releases much more energy than most fusion reactions.
DT fusion produces a neutron and a helium nucleus. Matteo Barbarino IAEA Department of Nuclear Sciences and Applications. Nuclear Fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission reaction in which heavy elements diffuse and form lighter elements.

Nuclear Fusion Could Give The World A Limitless Source Of Clean Energy We Re Closer Than Ever To It

Fusion Fission And Energy In Nuclear Equations Ib Physics Youtube

Nuclear Fusion Has Attracted More Than 2 Billion In Canary Media

Computational Modeling For Fusion Bsc Cns
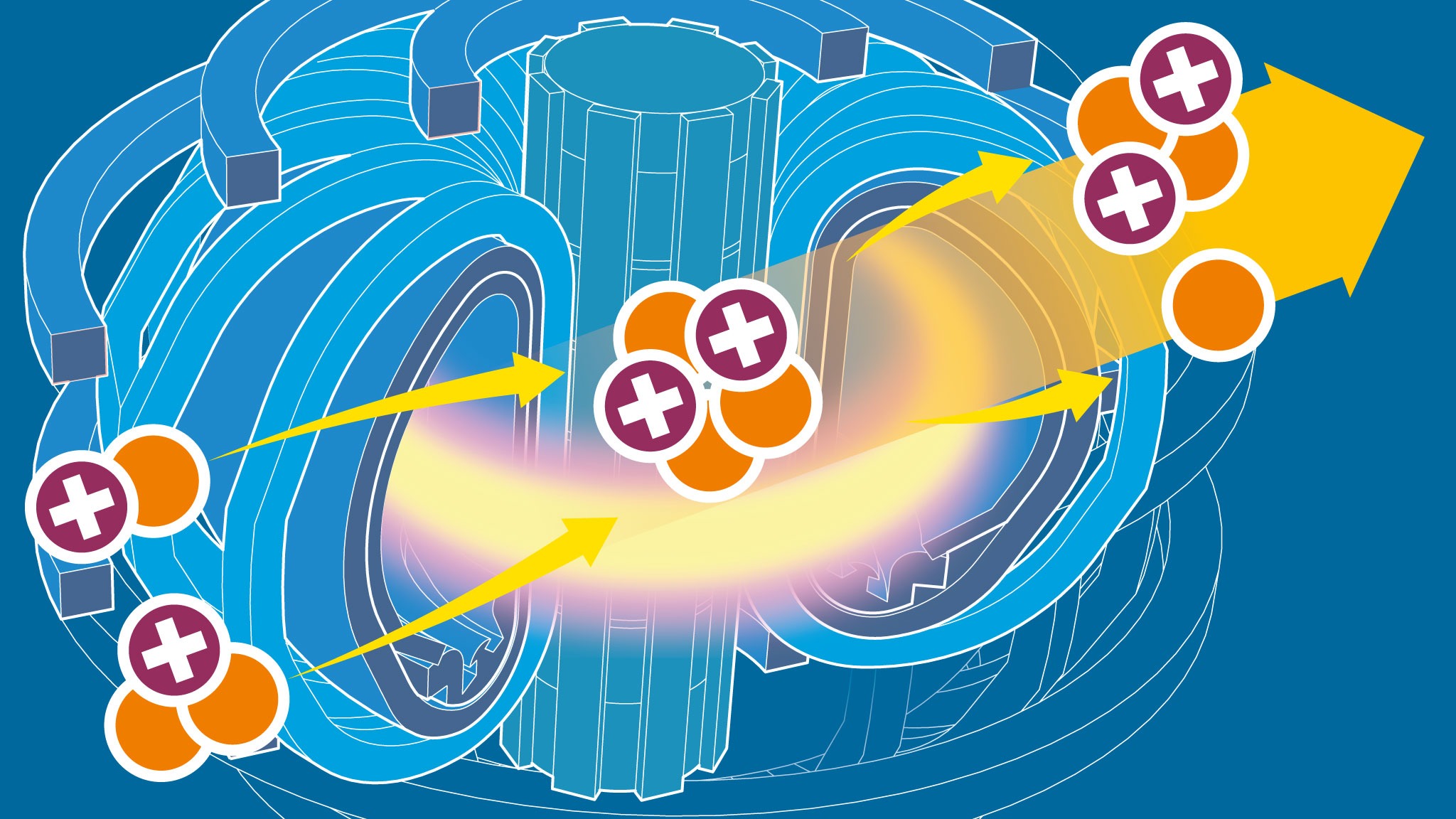
Nuclear Fusion Why The Race To Harness The Power Of The Sun Just Sped Up Financial Times
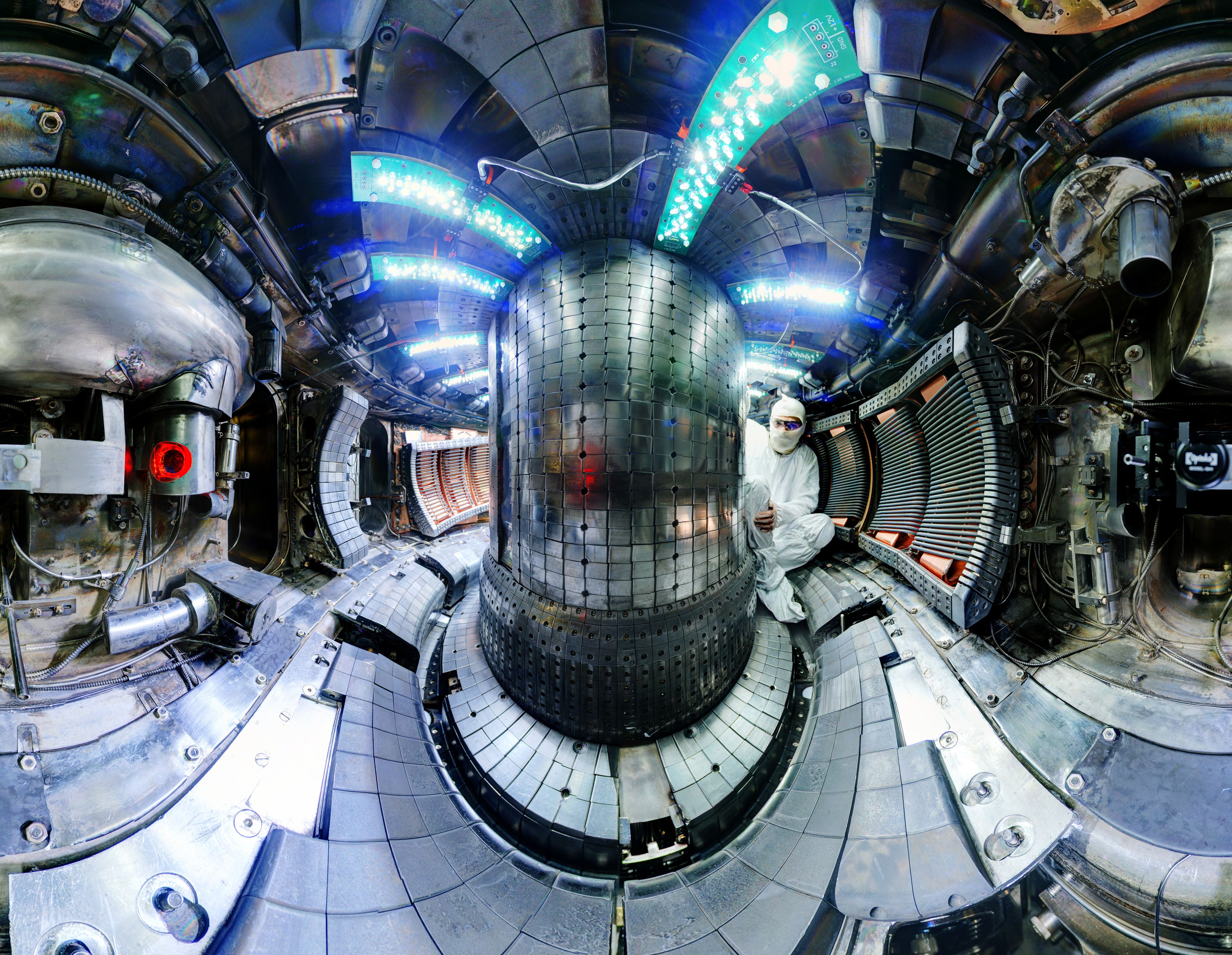
New Record For Fusion Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
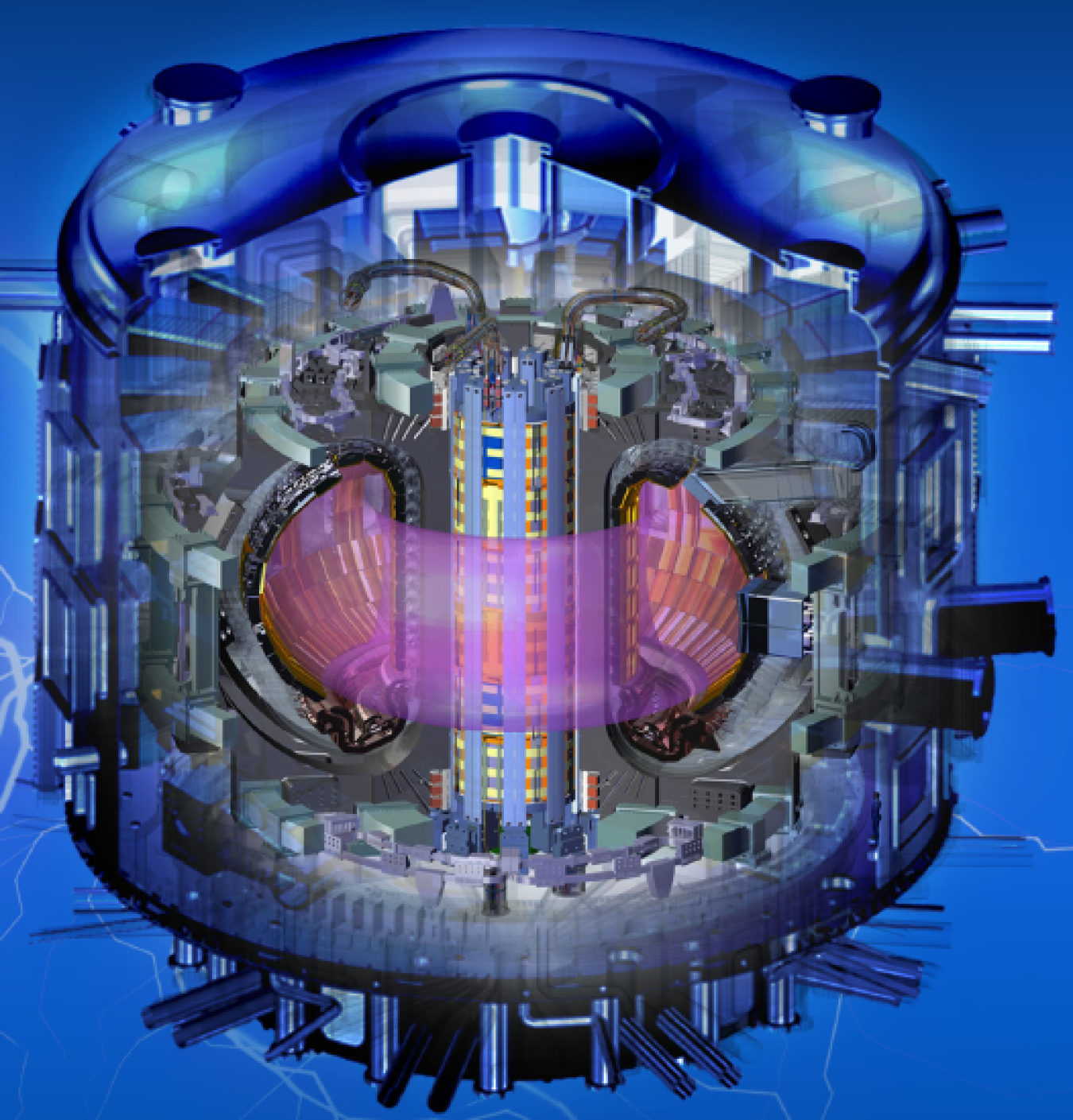
Doe Explains Fusion Nuclear Science And Technology Department Of Energy
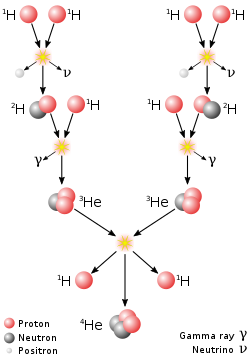
Nuclear Fusion Wikipedia

94pqq3j9dblypm
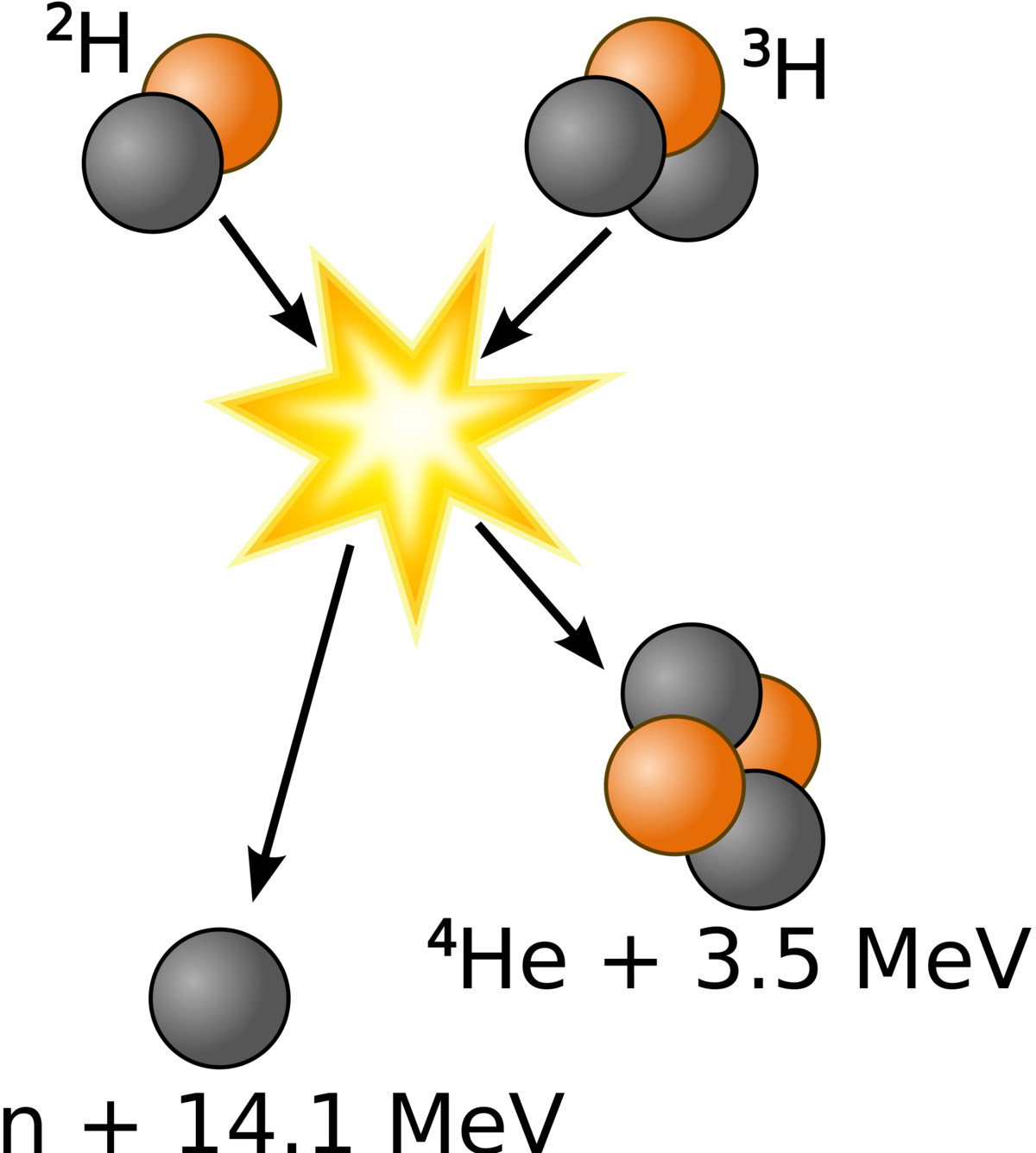
Nuclear Fusion Energy Education

Nuclear Fusion A New Source Of Clean Energy

Un 4 Zwvzmdrzm
Nuclear Fusion Power Could Be Here By 2030 One Company Says Live Science

Nuclear Fusion Graduate Texts In Physics Morse Edward Amazon De Books
Startups Take Aim At Nuclear Fusion Energy S Biggest Challenge Bloomberg

What Is Nuclear Fusion And Why The Hype Sciencealert
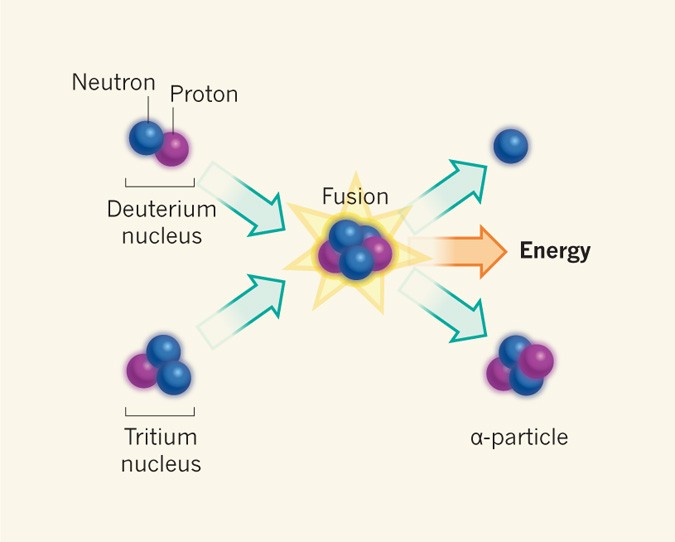
A Promising Advance In Nuclear Fusion Nature